The B2B Seller’s Guide to Ecommerce Payment Gateways
- 10 min read
Our guide explores what an ecommerce payment gateway is, how it works, and the benefits that ecommerce payment gateways offer to B2B sellers and merchants.
Online shopping is big business, accounting for 22% of retail sales around the globe. Six trillion dollars change hands online each year, and more than 81% of payments go through digital wallets, credit cards, and debit cards.
B2B merchants in the U.S. receive about 17% of their payments in digital form, up from 13% in 2019. This trend will continue as more B2B sellers make it easier for customers to pay online.
Ecommerce payment gateways are essential for making online payments possible. They expedite and simplify payments to the benefit of both consumers and merchants.
This article will explain what ecommerce payment gateways are, how they work, and why they’re important for B2B merchants.
Jump to a section of interest:
What is an ecommerce payment gateway?
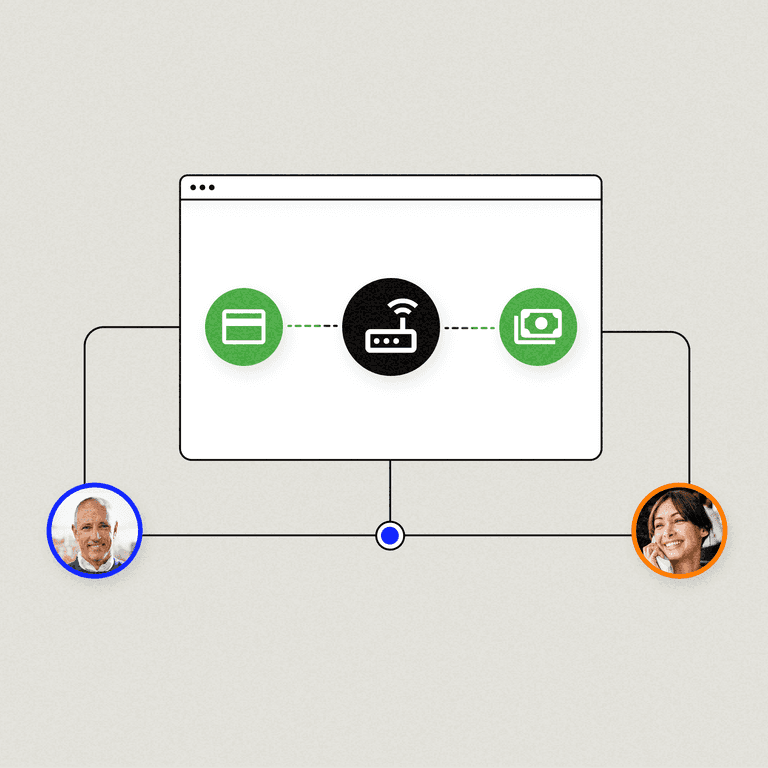
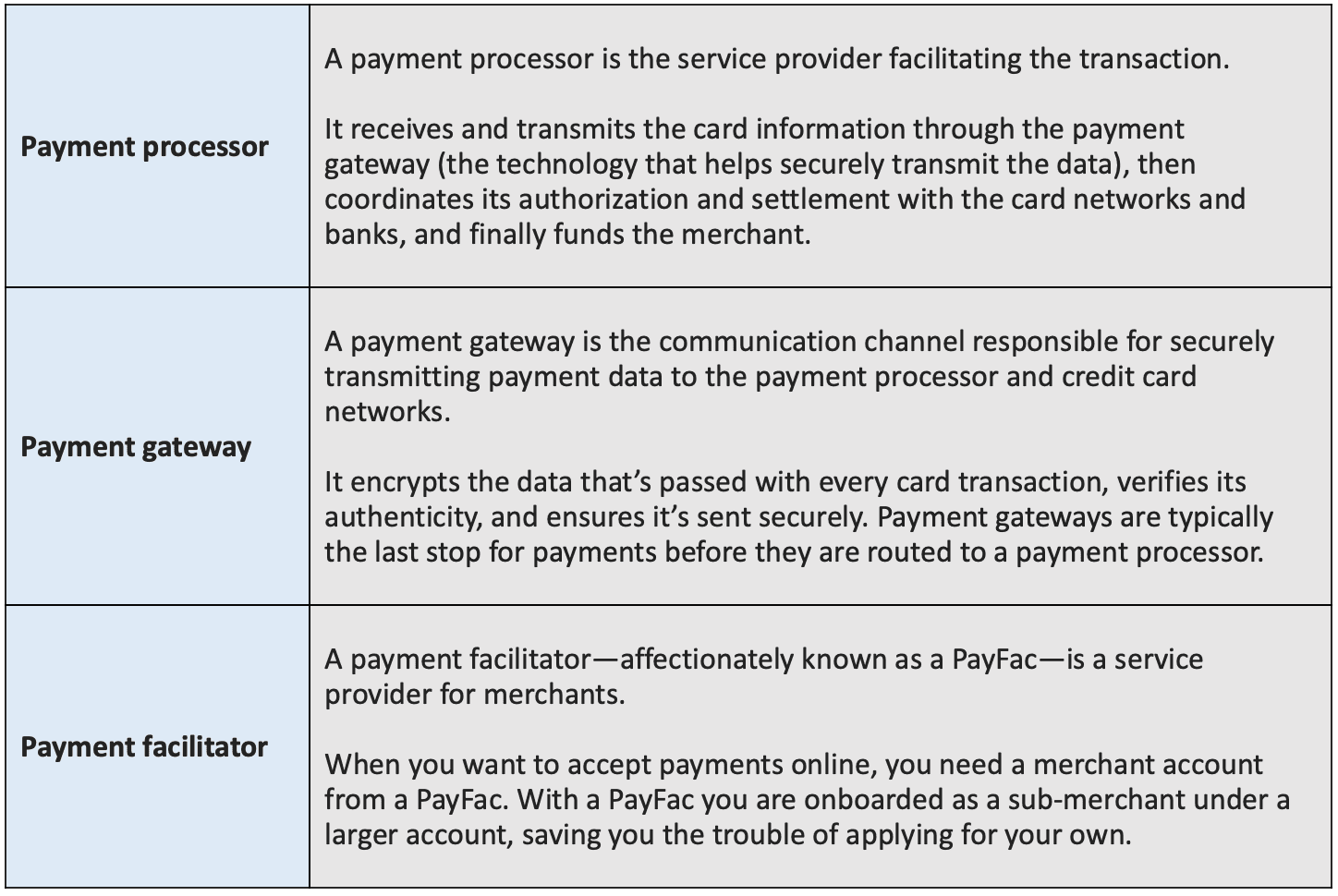
An ecommerce payment gateway is a secure communication channel for transmitting payment data and other sensitive information between payment processors (Apple Pay, PayPal, TSYS, First Data Merchant Services, Versapay, etc.), credit card networks, and banks. The technology facilitates approval and funding in just seconds.
Once a buyer enters their credit card information on a website, the payment gateway encrypts the data, verifies its authenticity, and routes it for verification, approval, and funding. Payment gateways are typically the last stop for payments before they’re routed for processing and approval.
Different types of payment gateways
Payment gateways can be self-hosted or hosted by a third party. Self-hosted configurations let your customers complete transactions on your website. Hosted configurations redirect customers to another site, such as PayPal, for transaction completion.
Within these two categories, retailers have a few different options:
1. On-site
On-site payment gateways use merchant servers to manage payments, providing greater control over the checkout experience. These gateways also come with more responsibility in terms of data security and server performance.
2. Check out on site, pay off site
In this scenario, checkout occurs on your website while processing happens in the gateway’s back end. While this configuration is simple and secure, merchants lose some control over the customer experience.
3. Redirects
This configuration lets customers use alternative payment options, such as digital wallets, by sending them to another page. While this setup is secure and convenient, especially for small businesses, it adds a second step for customers; and merchants have less control over the purchase experience.
Adding the extra step for customers may increase rates of cart abandonment.
4. Proprietary payment gateways
Some payment processors like Versapays have a proprietary payment gateway. The processor will accept payment, securely send payment data to card networks and banks, and fund the merchant.
While this setup is similar to the second option, it helps merchants focus on running their business without dealing with the nuances and logistics of payment processing. Plus, only one entity controls transaction flows, instead of multiple entities.
💡 If you’re evaluating payment processors—and are looking to start accepting payments online—consider those that bundle all the services a merchant needs to accept payments, including equipment and support for setting up a merchant account. Here’s an excellent guide for understanding the differences between payment gateways, processors, and facilitators.
What are some examples of payment gateways?
Popular payment gateways include:
Beanstream/Bombora
Chase Paymentech (Orbital)
Heartland Payments
USAePay
CardConnect
How do ecommerce payment gateways work?
When a buyer orders something online, the ecommerce payment gateway identifies the appropriate credit card network (AMEX, Visa, etc.) and routes the transaction details to a payment processor.
From there, the request goes through the payment gateway to the issuing bank, which determines the legitimacy of the purchase and checks the buyer’s credit. If approved, the payment gateway sends the transaction to the merchant’s bank for immediate funding.
From credit card to cash received
How ecommerce payment gateways manage online payments:
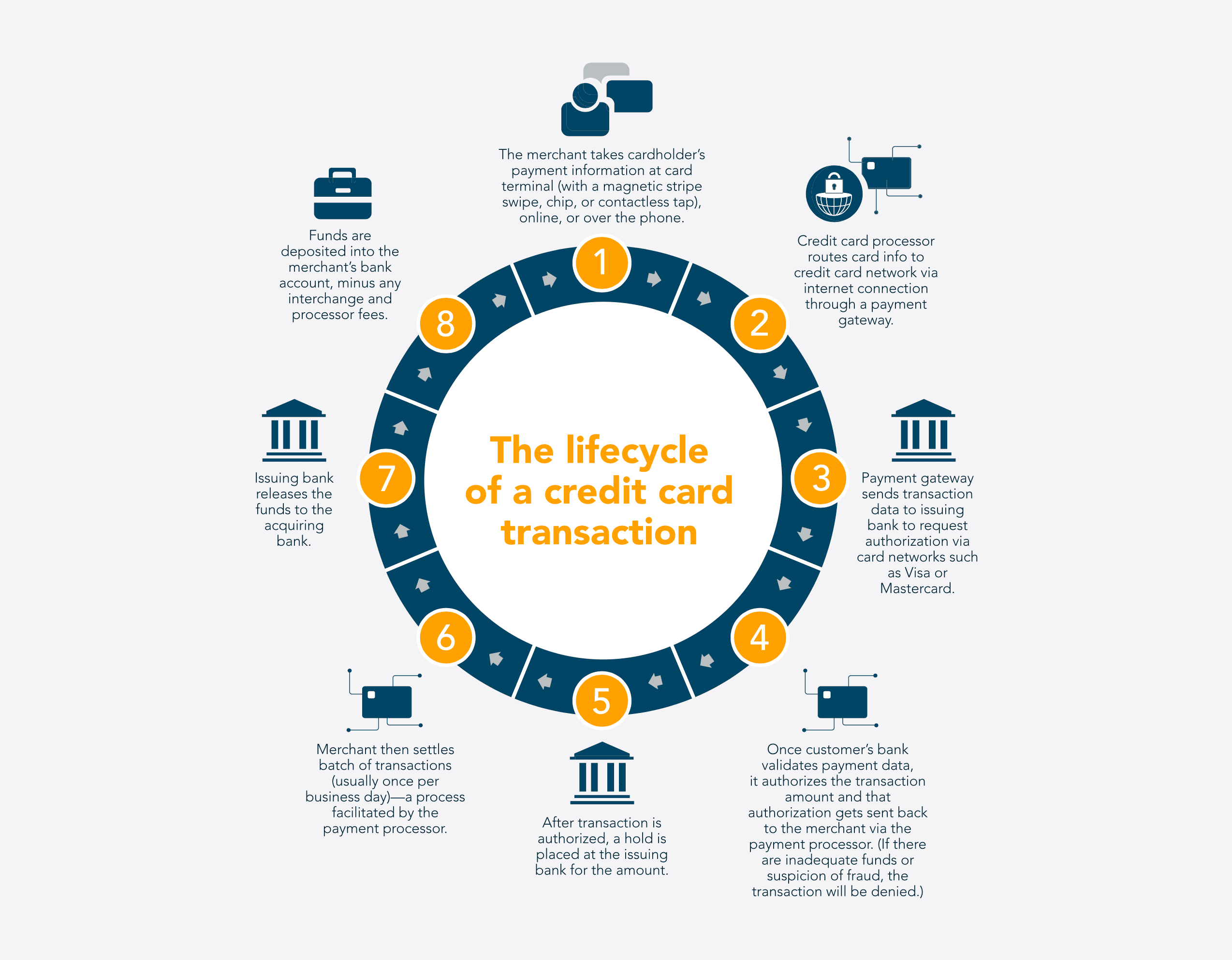
Step 1: The merchant takes the cardholder’s payment information at a card terminal (with a magnetic stripe swipe, chip, or contactless tap), online, or over the phone.
Step 2: Credit card processor routes card info to credit card network via internet connection through a payment gateway.
Step 3: Payment gateway sends transaction data to the issuing bank to request authorization via card networks such as Visa or Mastercard.
Step 4: Once the customer’s bank validates payment data, it authorizes the transaction amount and that authorization gets sent back to the merchant via the payment processor. (If there are inadequate funds or suspicion of fraud, the transaction will be denied.)
Step 5: After a transaction is authorized, a hold is placed at the issuing bank for the amount.
Step 6: Merchant then settles a batch of transactions (usually once per business day)—a process facilitated by the payment processor.
Step 7: Issuing bank releases the funds to the acquiring bank.
Step 8: Funds are deposited into the merchant’s bank account, minus any interchange and processor fees.
Besides ensuring the smooth and secure transmission of payment information, ecommerce payment gateways often come with valuable reporting and analytics capabilities, fraud detection services, and chargeback management services.
Why are ecommerce payment gateways important for B2B sales?
Ecommerce payment gateways are necessary for letting customers pay you in a way that’s easy and convenient for them. Essentially, payment gateways make your customers more likely to do business with you and help your business get paid faster.
Payment gateways also protect sensitive financial information, which gives your customers greater peace of mind and helps your business maintain its good reputation. With the right ecommerce payment gateway in place, digital payments are much more secure than old-fashioned payment methods like checks, wire transfers, and phone-initiated payments.
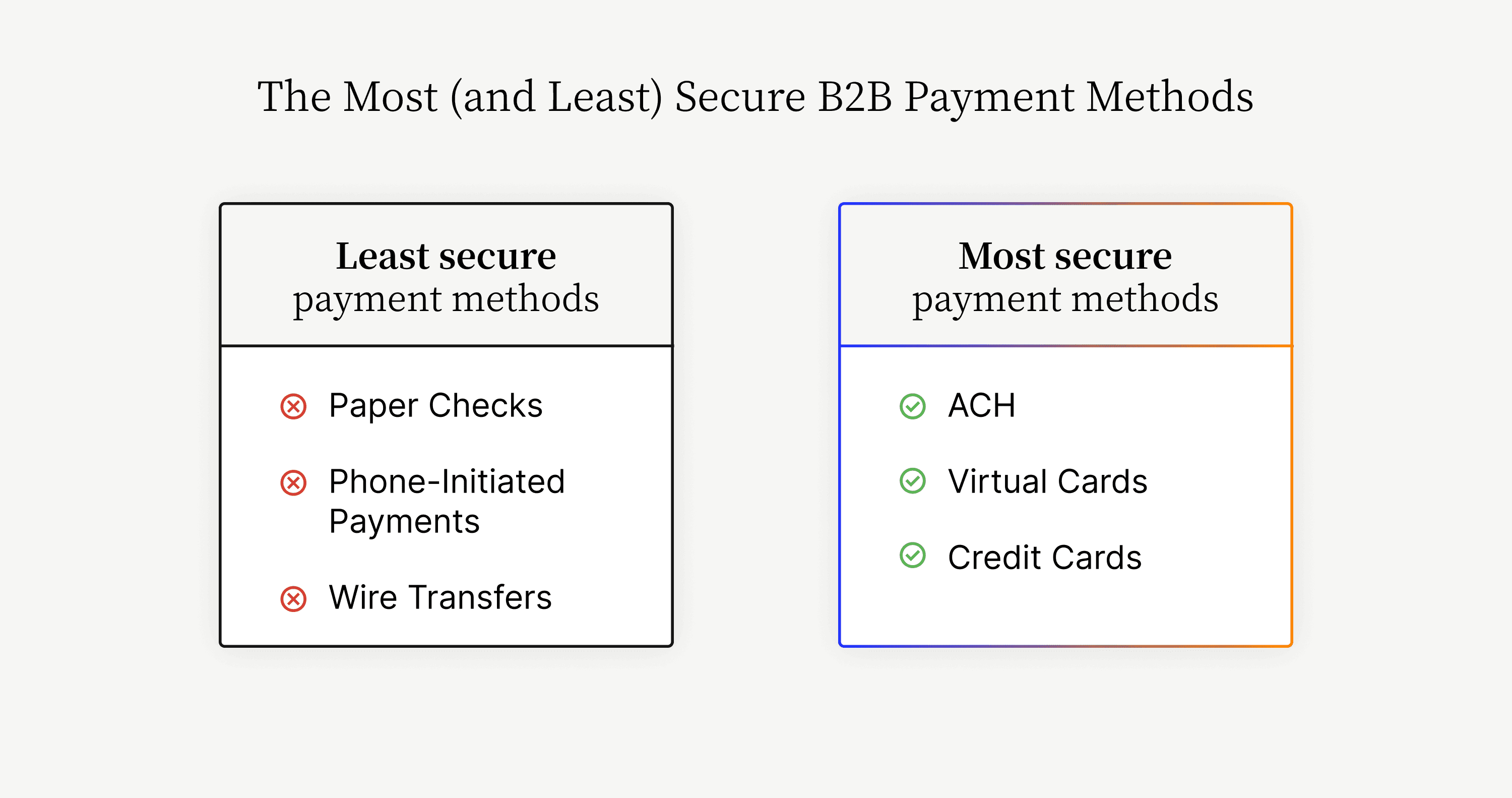
Greater revenue potential is another reason why B2B sellers are embracing digital payments that rely on payment gateways for fast and secure transmission and settlement. Because 70–80% of B2B decision makers prefer digital self-service, and because 60% of financial professionals are likely to convert most supplier payments from checks to electronic payments, offering digital payments can increase revenue by nearly 30%.
Another factor to consider is customer satisfaction and the time your business spends on invoice disputes. By giving customers a digital payment option that’s handled securely and completed in seconds by an ecommerce payment gateway, you can effectively eliminate costly and frustrating invoice disputes.
A Versapay report, based on a survey of 1,000 C-level executives, found that traditional payment processes are weak spots in the B2B customer journey. Seventy-three percent of respondents acknowledged that their invoice-to-cash cycle often causes negative customer experiences: When customers pay digitally, this essentially becomes a non-issue.
💡 The takeaway: Customers expect convenience, security, and service when purchasing products and services. An ecommerce payment gateway makes all that possible for online orders.
3 ways ecommerce payment gateways help B2B merchants
Ecommerce payment gateways present many benefits to B2B merchants, including:
Improved customer payment information security
Quick and easy setup
Seamless customer experience
Digital fraud protection
1. Improved customer payment information security
Building and maintaining a payment acceptance and processing system that protects customer information is time- and resource-intensive. Relying on a payment gateway that has security and PCI-DSS compliance baked in is one less concern for merchants. Plus, removing manual tasks like these creates a more streamlined accounts receivable process and increases team efficiency.
2. Seamless customer experience
By offering convenient, digital payment options, merchants will help customers pay easier and faster. Because B2B payments can be quite large, manual methods like paper checks can hold up payments for weeks, or even months. Digital payments, made possible through ecommerce payment gateways, eliminate these obstacles.
3. Digital fraud protection
Protecting your business from chargebacks and disputes is crucial for protecting your bottom line. Payment gateways can implement measures such as address verification service (AVS), card verification value (CVV) verification, payer authentication, and more.
Ecommerce payment gateways help B2B merchants implement payment systems that are convenient and effective for themselves and their customers.
—
💡 Read our guide on digital payment fraud prevention to learn how B2B merchants can fight fraud and maximize customer experience. Plus, learn why an integrated payments solution—with a proprietary payment gateway—embedded seamlessly with your ERP is crucial to preventing payment fraud.
Frequently asked questions about ecommerce payment gateways
How much do ecommerce payment gateways cost?
Payment gateways charge a fee for their services, which can be a percentage of the transaction amount or a flat fee per transaction.
Can ecommerce payment gateways help with fraud detection?
Yes. Sometimes, payment gateways temporarily hold a part of payments to keep a margin for fraud claims and chargebacks. Integrating address and card verification systems with your payment gateway can also help reduce your fraud risk.
What’s the best payment gateway?
Many ecommerce payment gateways are available, so it’s important to do your due diligence. We recommend choosing a payment processor with its own payment gateway. A single processor controls the entire transaction flow instead of bringing in another third party.
What’s the difference between an ecommerce payment gateway and a payment processor?
A payment processor receives and transmits payment information through the payment gateway to coordinate authorization and settlement. A payment gateway is the communication channel.
About the author
Ben Snedeker