Paper Invoices vs. Electronic Invoices: Differences, Pros, and Cons
- 7 min read
This article looks at the differences between paper and electronic invoices. Learn how each invoicing process differs, along with the benefits and cons of each.
Invoicing is one of those financial processes that sounds simple, but can actually be quite complicated, costly, and time-consuming for businesses. The more manual the process, the more opportunities for mistakes in creating, sending, and reconciling invoices.
No matter how your organization invoices, an efficient invoicing process manifests three clear benefits:
Better cash flow management through timelier payments
Higher customer satisfaction, as effective invoicing build trust and professionalism
Reduced disputes and payment delays
In this article, we’ll explore the differences between paper and electronic invoices. We’ll demonstrate the differences in both invoicing processes and provide a thorough understanding of the pros and cons of each. Click below to jump to a section of interest.
Everything you need to know about paper invoicing:
Everything you need to know about electronic invoicing:
Everything you need to know about paper invoicing
What is paper invoicing?
Paper invoicing refers to the traditional method of generating and distributing printed physical invoices. It involves manual processes and physical documentation. Hard copy invoices also require physical delivery via courier or mail, and a physical return of paper payment (i.e., check).
Because this process is almost entirely manual, it can be particularly prone to error. Notably, human error is the most significant cause of invoice disputes, making paper invoicing a primary culprit of delayed payments:
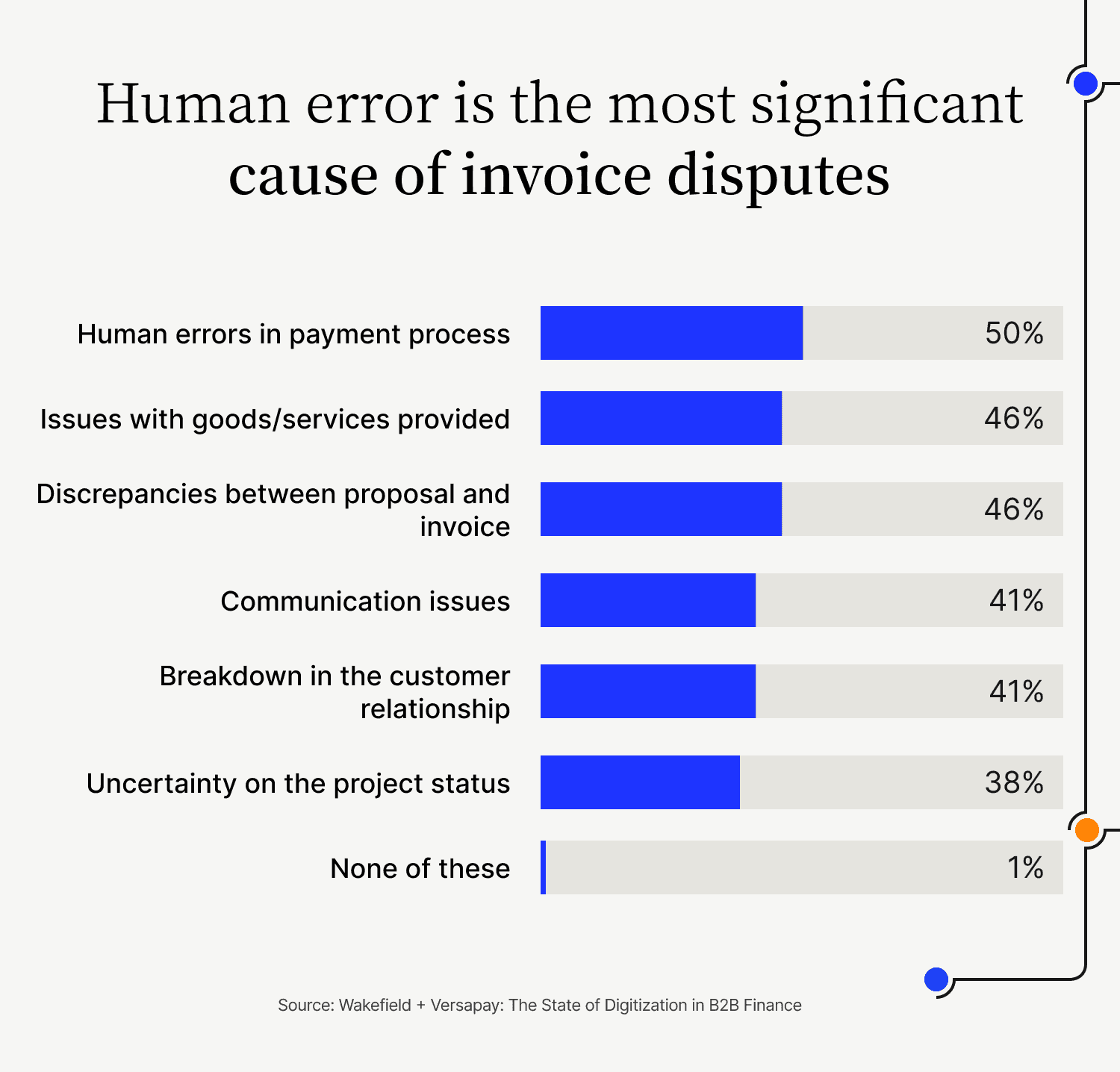
How does paper invoicing work?
Paper invoicing includes many manual steps, including generating and printing invoices, packaging and distributing them, receiving and reviewing invoices, processing payments, reconciling, archiving, and following up when necessary.
Steps 1 & 2: Generate and print invoices
Businesses often use spreadsheets, software, or dedicated invoice templates to build invoices. Invoices must include specific information like amount due, due date, and payment terms. Businesses will print invoices themselves or outsource to a third party.

Steps 3 & 4: Package and distribute invoices
After printing, invoices must be organized and placed in envelopes with any supporting documentation. Envelopes must be addressed, sealed, posted, and mailed.
Step 5: Customer receives and reviews invoice
After receiving the paper invoice in the mail, the customer will review it for accuracy and compare it with the corresponding purchase order or contact. The customer’s AP department will either approve the invoice or contact the business to dispute an issue, which could cause a payment delay.
Step 6: Pay and process invoice
To initiate payment, the customer prepares to pay via their preferred payment method, either paper check, bank transfer, or cash payment. (Paper checks are one of the least secure B2B payment methods, yet most encouraged when invoicing manually.)
Steps 7 & 8: Reconcile, archive, and store
After the payment has been received, the business matches it to the corresponding paper invoice and updates the accounts receivable ledger to record the payment and mark the invoice as paid. Invoices are stored in file cabinets or other archives to ensure proper record-keeping.
Step 9: Follow up and collect where necessary
When payments become overdue, businesses must follow up with customers to remind them of their outstanding invoice. If invoices become delinquent, the business must initiate collection procedures to ensure payment.
Pros and cons of paper invoicing
Here’s a quick checklist of the pros and cons of paper invoices:

As you can see, the list of cons heavily outweighs the pros. That’s because paper invoicing is manual, inefficient, and unmanageable at scale. Here are 10 reasons why paper-based invoicing is bad for business.
Everything you need to know about electronic invoicing
What is electronic invoicing?
Electronic invoicing is the process of sending invoices in a digital format. Electronic invoices, or e-invoices, streamline the invoicing process, reduce costs, and enhance overall AR efficiency.
How does electronic invoicing work?
There are different levels—or tiers—to electronic invoicing. Manually emailing invoices is the most basic level; it then progresses to posting a digital invoice in a customer-facing online payment portal or to a customers’ accounts payable portal.
Collaborative accounts receivable payment portals like Versapay’s offer businesses and consumers convenient visibility into invoices, payment history, account status, and more.
Step 1: Generate and send invoices
Create invoices in your ERP and post them automatically to your AR automation platform. Invoices can be personalized with company branding and relevant information. AR teams can send invoices instantly via email or post them directly to an accounts receivable payment portal, where customers can access them 24/7.
With some automation platforms, electronic invoices can be posted directly to a customer’s account payable portal.
Steps 2 & 3: Customer receives and pays invoice
The customer receives the invoice through their personalized invoice delivery channel where they can easily review invoice details to compare it with the purchase order or other records. They can also download or print the invoice if needed.
When invoicing electronically, supporting documentation is easy to attach to the email or through the payment portal, making it easy for both customers and AR teams to reference the information they need in one place. This direct communication between businesses and customers also accelerates the collections process.
Customers are encouraged to initiate electronic payments through the payment portal or directly on an electronic invoice received in the mail, via credit or debit card, ACH or EFT, virtual credit cards, or bank transfer. Payment details are included directly in the electronic invoice to simplify the process. Customers can more easily make short payments against electronic invoices, too, and some payment portals that host electronic invoices allow customers to comment directly on line items to address discrepancies or surface a dispute.
Steps 4 & 5: Reconcile, record, and store
After the business receives notification that payment has been received, they can easily reconcile it with the electronic invoice. Payments made through cloud-based payment portals—like some AR automation platforms offer—are automatically matched to the related outstanding invoice, eliminating the need for manual reconciliation.
Integrations between invoicing and account systems ensure payments are automatically posted back to your ERP system, enabling real-time insight into cash flow. All invoices and payments are stored in digital databases or cloud storage for easy access and retrieval, simplifying auditing and financial reporting.
In the event of past-due accounts, top-tier AR automation platforms will allow you to configure and send online payment reminders, reducing manual collections efforts—that are so prevalent in manual invoicing processes.
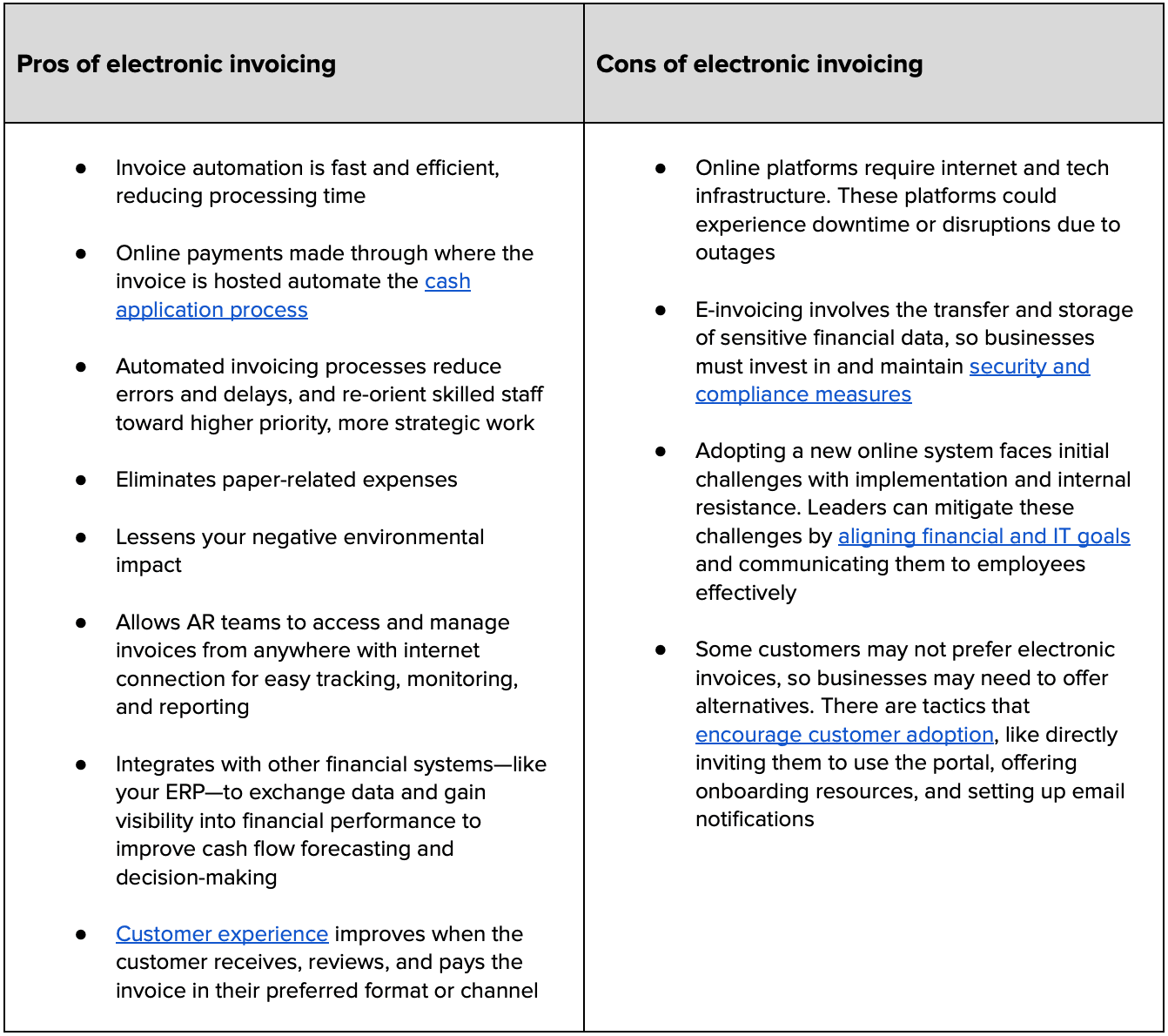
Pros and cons of electronic invoicing
Let’s break down the pros and cons of electronic invoicing solutions:
Deliver invoices to customer preferences with Versapay
Versapay offers a world-class omni-channel invoicing system that delivers invoices according to customer preferences. This system lowers invoicing costs, increases digital invoice acceptance, and captures payments faster.
The online payment portal Versapay offers allows businesses to provide a secure, convenient electronic invoice presentment and customer payment option. Teams can automate every AR process, from order to cash to collections, and accept payment types across a host of diverse channels.
By offering real-time visibility to account information and direct collaboration for dispute resolution, Versapay helps businesses achieve high customer satisfaction while increasing cash flow at the same time.
About the author

Jordan Zenko
Jordan Zenko is the Senior Content Marketing Manager at Versapay. A self-proclaimed storyteller, he authors in-depth content that educates and inspires accounts receivable and finance professionals on ways to transform their businesses. Jordan's leap to fintech comes after 5 years in business intelligence and data analytics.